Multiple sclerosis
It is an autoimmune condition in which the cells of the immune system of the body mistakenly attack the myelin sheath of nerves of brain , spinal cord etc. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder of nervous system which has no cure but manageable with medications .
updated on:2025-01-10 06:54:53
Written by Dr. Sanjana V.B Bhms,dbrm,cdn
Founder & medical director of siahmsr wellness.in
All rights reserved with siahmsr digital healthcare[siahmsr wellness]
Reviewed by SIAHMSR medical team
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS [MS]
Multiple sclerosis
is a neurological disease affecting mostly young people between the ages of 20
to 40 years, although no age is exempt from it. This disease affects nerve
sheaths of eyes, brain and spinal cord causing loss of vision, muscle weakness
and paralysis & some variants of this disease may progress to death
rapidly.
It is an autoimmune
condition in which the cells of the immune system of the body mistakenly attack
the myelin sheath of nerves of brain, spinal cord etc. Myelin is a protective
covering or sheath over the nerve fibers.
“Multiple sclerosis”
refers to the "numerous areas of scar tissue" resulting from the
attack on myelin by the immune system. Inflammation of nerves is the hallmark
of multiple sclerosis [MS].
What are the causes of multiple sclerosis?
Genetic
This neurological disease is linked to genes. Studies show
that multiple sclerosis runs in families. Women are mostly affected with this
condition.
Smoking
Smoking can worsen the severity of disease. People who smoke tend to have more brain lesions and brain shrinkage than non-smokers.
Epstein–Barr virus
It is linked with Epstein Barr virus infection also. Studies have provided evidence that multiple sclerosis (MS) is a rare complication of infection with the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV]. The risk of MS increases markedly after infectious mononucleosis (symptomatic primary EBV infection) and with high titres of antibodies to specific EBV antigens in people affected with the virus.
How does multiple sclerosis affect nervous system?
Neurons (nerve cells) are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, which receives and transmits signals throughout body and are vital for the sensory and motor functions of body.
A neuron has three
main parts: dendrites, an axon, and a cell body.
In Multiple sclerosis immune cells of the body mistakenly
attacks myelin covering of axons of nerve cells in the central nervous system.
The myelin sheath covered nerve groups are commonly called white matter.
MS can also damage the nerve cell bodies, which are found in the brain's gray matter, as well as the axons themselves in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves that transmit visual information from the eye to the brain. As the disease advances the grey matter and outer cortex area of brain is also affected.
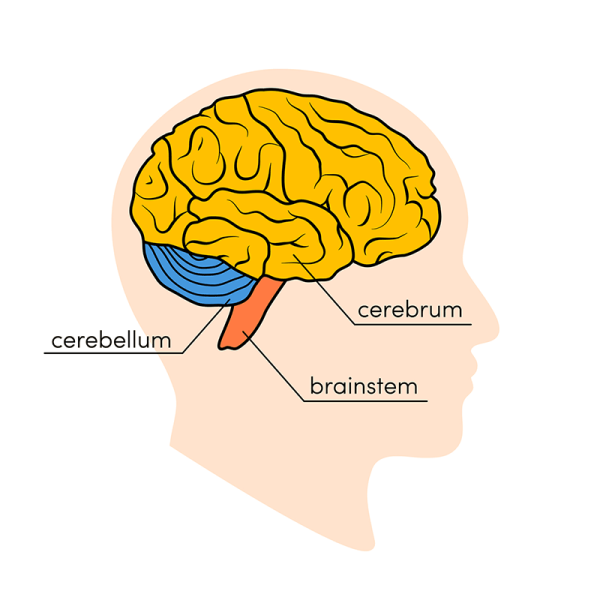
The severity of
multiple sclerosis symptoms is based on the intensity of inflammatory reaction
as well as the location and extent of the plaques, which primarily occur in the
brain stem, cerebellum , spinal cord, optic nerves, and the white matter around
the brain ventricles.
Multiple sclerosis
impacts people differently and symptoms manifested range from mild to severe.
In some people the disability caused by myelin sheath destruction of nerves
worsens overtime.
Most people with MS, will experience short periods of symptoms followed by long symptom free intervals or period of dormancy.
What are the signs & symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis vary from person to person
depending on the area of brain affected and intensity of inflammatory response.
There are four main types of Multiple sclerosis [MS]:
· Relapsing-remitting MS
Symptoms appear and
disappear in this type of MS. In between attacks, there is remission and people
return to normalcy or to their usual level of disability.
The period of intense symptoms is called an attack, a
relapse, or exacerbation. The periods of disease inactivity between MS attacks
are referred to as remission. The period of attack and remission always
alternate with long intervals of time in between these. Most people with MS are
initially diagnosed with this form of the disease.
· Secondary-progressive MS
In this type of MS, disease comes to a steady phase with
history of MS attacks in the past. Now start developing gradual and steady
symptoms and deterioration in their function over time.
· Primary-progressive MS
This type of MS is
not seen often. It presents with progressively worsening symptoms from the
beginning itself with no relapses or exacerbations. There might be short
symptom free intervals sometimes in this type of MS.
· Progressive-relapsing MS
This very uncommon type of MS has steady worsening of symptoms from the beginning with acute relapses that can occur over the course of disease.
Rare variants of Multiple sclerosis which
progress rapidly are:
1 .Marburg variant MS (also known as malignant MS) is characterized by sudden and steady occurrence of symptoms with decline in functions. This variant can cause marked disability or it can cause death soon.
2. Balo's concentric sclerosis is characterized by presence of concentric rings of myelin destruction in MRI scan of brain. This variant of MS also can progress rapidly.
Symptoms & signs of multiple sclerosis
Early symptoms of multiple sclerosis
· Eyes are affected in this disease early. Multiple
sclerosis may cause blurred vision or double vision. Inflammation of the nerves
of eye [optic neuritis], causes pain with eye movement and rapid vision loss.
· Musculoskeletal system is also affected soon: Muscle
weakness of hands and legs, and muscle stiffness accompanied by painful muscle
spasms may occur.
Other symptoms
include:
Tingling,
numbness, or pain in the arms, legs, trunk, or face. Clumsiness, especially
difficulty in maintaining balance when walking.
· Bladder
control is difficult.
· Intermittent
or constant dizziness
· Mental
or physical fatigue
· Later
symptoms of multiple sclerosis
· depression
or difficulty with emotional control
· difficulty
in concentrating, multitasking, thinking, learning
· problems
with memory or judgment
· Muscle weakness, stiffness, and spasms causing difficulty in walking or standing.
· Partial or complete paralysis in individuals who are untreated or have advanced disease.
· Exacerbation
of symptoms may occur following common infections.
· Pain
is a major symptom as MS affecting nerves of eyes and face [optic neuritis and
trigeminal neuralgia].
· Pain
and spasms of lower limbs and sharp pain shooting down the legs or around the
abdomen can happen.
· Transverse myelitis (an inflammation of the spinal cord) may develop in those with MS.
The symptoms
include sudden onset of lower back pain, muscle weakness, abnormal sensations
in the toes and feet, or difficulties with bladder control or bowel movements.
This can rapidly progress to more severe symptoms, including arm and/or leg paralysis. In most cases, people recover at least some function within the first 12 weeks after an attack begins.
Complications of Multiple sclerosis
· Optic
neuritis or inflammation of nerves to eyes cause blurred or grayed vision,
temporary blindness in one eye, loss of normal color vision, depth perception,
or loss of vision in parts of the visual field.
· Uncontrolled
horizontal or vertical eye movements (nystagmus), “jumping vision"
(opsoclonus), and double vision (diplopia) are common in people with MS.
· Muscle
weakness and spasticity is common in MS. Physical inactivity can worsen
stiffness, weakness, pain, fatigue, and other symptoms.
· Tremor,
or uncontrollable shaking.
· ataxia—unsteady,
uncoordinated movements—due to damage to the areas of the brain that coordinate
muscle balance.
· Sexual
dysfunction can result from damage to nerves running through the spinal cord.
Sexual problems may also arise from MS symptoms such as fatigue, cramped or
spastic muscles, and psychological factors
· Cognitive
impairment—a decline in the ability to think ,remember ,understand etc. affect
around 75 percent of people with MS.
· Depression
· Difficulty
in swallowing
· Reduced
capability to care for self
· Urinary
incontinence & infections.
· Osteoporosis
or thinning of the bones
· Pressure
sores
· Side
effects of medicines used to treat the disorder
Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
In addition
to a complete medical history, physical examination, and a detailed
neurological examination, different tests are conducted to rule out other
similar neurological problems and confirm the diagnosis of MS.
The disease
is confirmed when symptoms and signs develop and are related to different parts
of the nervous system at more than one different interval and after other
alternative diagnoses have been excluded.
Tests to
diagnose MS are:
Lab
investigations
Blood tests
to rule out other conditions that may resemble MS.
Lumbar
puncture (spinal tap) for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests, including CSF
oligoclonal banding may be needed.
Imaging
studies:
MRI scan of
the brain or the spine, or both are important to help diagnose and follow MS.
Nerve
function study (evoked potential test, such as visual evoked response) is less
often used.
Treatment for multiple sclerosis
There is no known permanent cure for this disease. However
it is manageable with medications.
The available treatment methods aim at symptomatic
management. Treatments can reduce the number and severity of relapses and delay
the progression of the disease to disabilities.
Medications
· Corticosteroids- may help to suppress the immune system
and reduce inflammation.
· Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) can treat severe
flare-ups in people with relapsing forms of MS who do not have a good response
to methylprednisolone. However ,it is not effective in all types of MS.
· Beta interferon drugs are among the most common
medications used to treat MS. Interferons are signaling molecules that regulate
immune cells.
· Natalizumab, Ocrelizumab, Mitoxantrone etc. are a few
drugs used for different types of MS.
· Trigeminal
neuralgia (facial pain) is treated with anticonvulsant or antispasmodic drugs,
or less commonly, painkillers.
Other helpful interventions for managing multiple sclerosis
· Physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy,
and support groups may help the people with disabilities resulting from
multiple sclerosis.
· Assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, bed lifts, shower
chairs, walkers, and wall bars etc. may
help to do the life's routine activities with independence.
· Spinal devices may help to decrease the pain and
spasticity in the legs
· A well-planned exercise program early in the course of
the disorder is useful.
· A healthy lifestyle, with good nutrition and enough rest
and relaxation
· Mind body relaxation exercises such as simple yoga poses.
· Vitamin D and other essential nutrient supplements such
as vitamin B12 are good for managing MS
Complementary &alternative medicine
Acupuncture is used for some spine related problems.
Homeopathy
According to a research study [5]some homeopathic remedies
are used frequently for managing Multiple sclerosis symptoms and these include:
Bladder symptoms and urinary retention managed with
Causticum.
Bowel dysfunction, mainly constipation, may be treated by
Opium, Alumina, Nux vomica, and sulphur.
Daily use of phosphorus has been reported to be helpful for
optic neuritis; combination with Hypericum makes it more effective.
Gelsemium for double vision.
Cuprum metalicum, Cuprum arsenicum, Nux vomica and Ignatia
for cramp and spasm.
Secale for sensory symptoms have been reported to be
effective in MS patients.
Ayurveda
Some Ayurvedic medications along with lifestyle changes,
diet and yoga may be helpful in managing symptoms of Multiple sclerosis.
Complementary and alternative medicines may be used as an
adjuvant therapy to improve the quality of life reducing the symptoms from
nerve inflammation.
How does exposure to sunlight help to prevent
multiple sclerosis?
Sun exposure may mitigate the incidence as well as severity and relapse of multiple sclerosis. The research studies points out that people who get exposed to sun every day and having higher levels of vitamin D in their blood are less likely to develop MS. Vitamin D is produced by exposure to sun from the skin cholesterol.
In people with MS also the severity of course of disease and relapses are considerably low if they get exposed to sun and get enough vitamin D. Moderate exposure to sunlight for 15-20 minutes a day helps human skin produce vitamin D. Studies state that vitamin D may help regulate the immune system in ways that reduce the risk of MS or autoimmunity in general.
copyright of the article - dr sanjanavb.
References
1. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41582-023-00775-5#:~:text=The%20link%20between%20IM%20and,an%20elevated%20risk%20of%20MS.
5.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2225411016302267


Recommended For You
Multiple sclerosis
It is an autoimmune condition in which the cells of the immune system of the body mistakenly attack the myelin sheath of nerves of brain , spinal cord etc. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder of nervous system which has no cure but manageable with medications .
Related Links

sdfgh